About the Profession
Who are Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologists?
They are highly trained health science professionals who help people of all ages and from all walks of life communicate better.
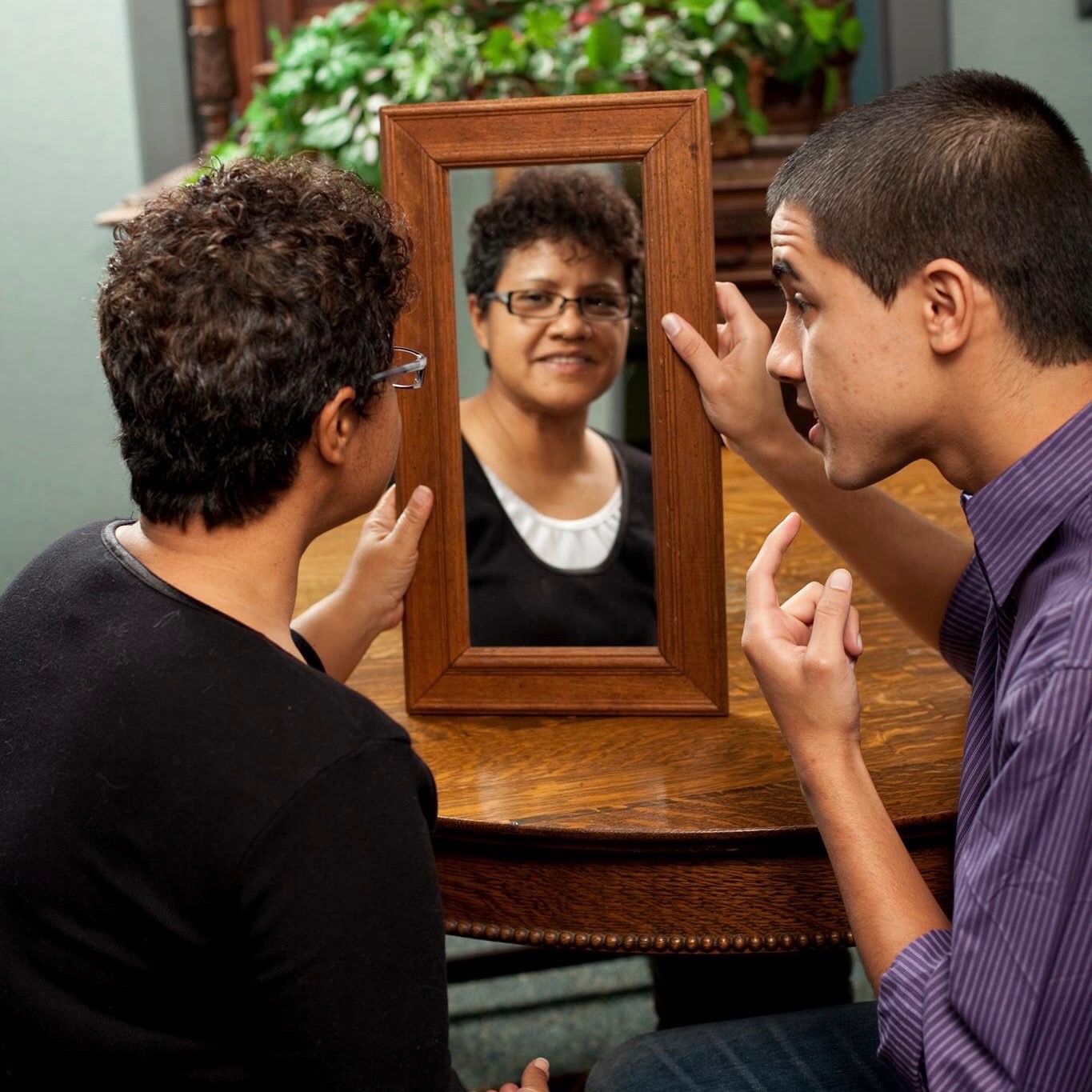 Roles & Responsibilities of Speech-Language Pathologists
Roles & Responsibilities of Speech-Language Pathologists
Speech-language Pathologists are individuals who treat, evaluate and conduct research in human communication and its disorders. They work with people of all ages, from infants to the elderly. As a speech-language pathologist, you would help people to:
- Learn proper sound production and fluent speech.
- Develop proper control of the vocal and respiratory systems for speech and swallowing purposes.
- Learn to express themselves and understand others.
- Relearn language and speech skills following a stroke or traumatic brain injury.
- Understand their speech or language disorder and help to achieve more functional communication abilities.
- Understand types and severities of communication disorders.
- Prevent speech and language disorders.
Roles & Responsibilities of Audiologists
Audiologists are professionals who specialize in the prevention, identification, treatment and management of individuals with hearing loss, balance problems, and central auditory processing problems.
They perform services which include the following:
- Evaluate hearing and the hearing mechanism using specialized equipment.
- Individualize the programming and fitting of hearing aids for people of all ages.
- Provide education and training in how to use hearing aids, assistive listening devices, and cochlear implants.
- Design rehabilitation programs to increase communication skills and provide counseling for hearing impaired individuals and their significant other.
- Evaluate work environments for hearing safety and education settings in order to optimize the environment for hearing impaired children.
- Work with children born with hearing loss, children who have acquired hearing loss early in life, and adults with acquired hearing loss due to disease or the aging process to facilitate the development of speech and language.
Career Possibilities
Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologists are in high demand in various professional settings such as:
- Hospitals
- Rehabilitation Centers
- Nursing Care Facilities
- Industry
- Home Health Agencies
- Long-Term Care Facilities
- Research Labs
- Center for Persons with Developmental Disabilities
- Public or Private Schools
- Private Practice
- Community Clinics
- College/University Clinics
- Health Department
- State or Federal Agencies
- Adult Day Care Facilities
- Business
These professionals work alongside teachers, physicians, physical therapists, social workers, psychologists, and other healthcare and educational professionals. Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologist are in demand for full-time employment as well as part-time and per diem opportunities.
Degree Certification & License Requirements:
Speech-Language Pathology – A Master of Science degree in Speech-LanguagePathology (MS/SLP) is necessary to begin work in the profession. A Speech-Language Pathologist must also be certified by the American Speech-Language and Hearing Association (ASHA) and may be required to hold state licensure depending on the state in which one chooses to work.
Audiology – A Doctorate in Audiology (AuD) is necessary to begin a profession as an audiologist. Audiologists must also be certified by the American Speech and Hearing Association (AHSA) and/or the American Academy of Audiology (AAA). Like their SLP counterparts, it may be required to hold state licensure depending on the state in which one chooses to work.
Job Outlook and Earning Potential
The future outlook for both speech-language pathology and audiology is excellent. Click on the degree name to see the latest report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Speech-Language Pathologist - Audiologist